Ankle Arthroscopy
What is Ankle Arthroscopy?
Ankle arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to diagnose and treat various conditions affecting the ankle joint. This advanced technique utilizes a thin fiber-optic camera called an arthroscope, which is inserted through small incisions in the skin. This allows the surgeon to visualize the internal structures of the ankle joint on a monitor, enabling precise treatment with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
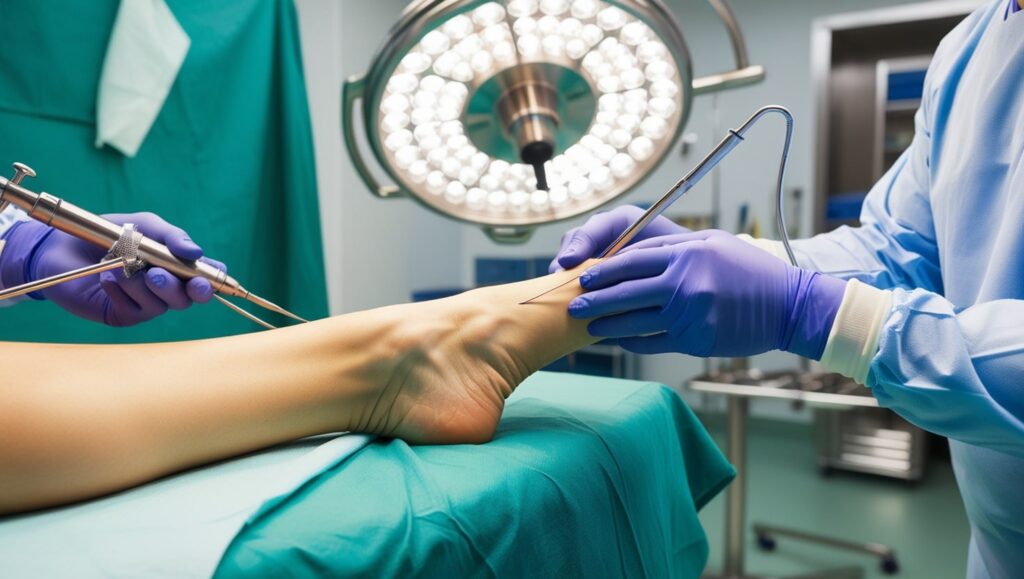
Why Is Ankle Arthroscopy Performed?
Ankle arthroscopy is commonly used to address a range of issues, including
- Injury Repair: Treatment of damaged ligaments, cartilage, or other structures resulting from trauma or repetitive strain.
- Removal of Loose Bodies: Extraction of loose fragments of bone or cartilage that can cause pain and limit mobility.
- Treatment of Ankle Impingement: Relief of pain caused by the abnormal contact between bones in the ankle during movement.
- Chronic Ankle Pain: Investigation and treatment of persistent pain when other non-surgical treatments have failed.
What to Expect During the Procedure?
Ankle arthroscopy is usually performed under regional or general anesthesia. The surgeon makes small incisions around the ankle and inserts the arthroscope along with specialized surgical instruments. The entire procedure generally takes about 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the complexity of the issues being addressed.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Post-operative care involves managing pain and swelling, along with specific rehabilitation exercises. Patients are often encouraged to begin gentle movements shortly after surgery to promote healing and regain range of motion. Your doctor will provide detailed instructions tailored to your recovery.


